Modifying Argo-CD
One of the benefits you get from using Argo-CD Autopilot is the bootstrap installation of Argo-CD. This means that Argo-CD will manage and reconcile itself based on the desired in your installation repository.
The state of Argo-CD is managed by the argo-cd application that is deployed by the autopilot-bootstrap application. The application is a kustomize type application and generates its Argo-CD manifests from bootstrap/argo-cd/kustomization.yaml.
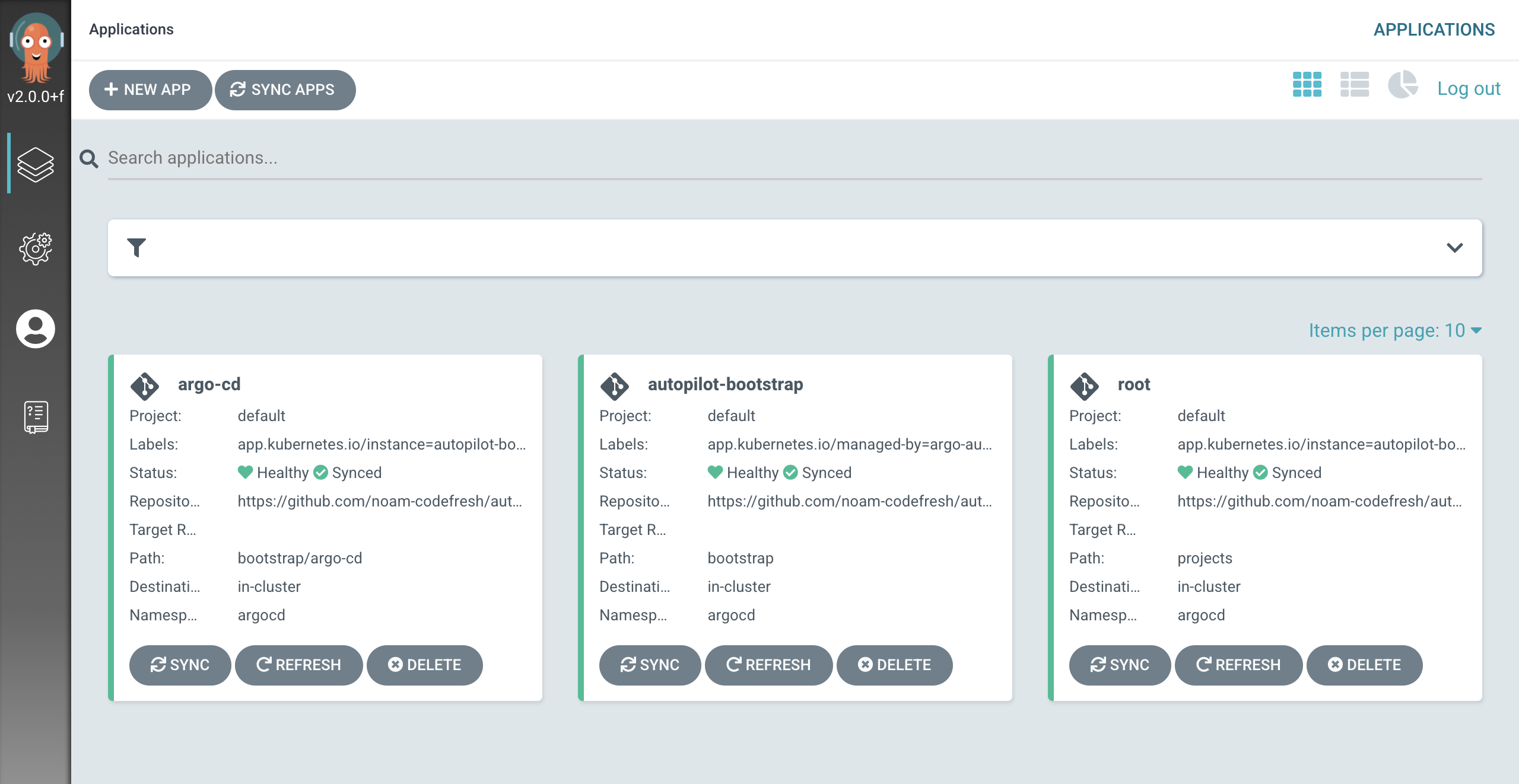 One of the applications you get after the initial bootstrap is the
One of the applications you get after the initial bootstrap is the argo-cd application
To modify your Argo-CD installation you would need to use the GitOps approach. This means you cannot modify Argo-CD resources directly in the cluster, instead you should use kustomize patches to modify the resources generated from bootstrap/argo-cd/kustomization.yaml.
Here are a few examples of common Argo-CD modifications:
Specifying Requests and Limits¶
The following shows the kustomization file in bootstrap/argo-cd/kustomization.yaml with patches which sets the requests and limits for argocd-repo-server and argocd-application-controller. Note that some parts of the file were omitted in this example.
You can use the same method to set requests and limits for any other Argo-CD component.
apiVersion: kustomize.config.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Kustomization
namespace: argocd
resources:
- github.com/argoproj-labs/argocd-autopilot/manifests/base?ref=v0.4.10
# Added these patches
patches:
- target:
group: apps
version: v1
kind: Deployment
name: argocd-repo-server
patch: |-
- op: add
path: /spec/template/spec/containers/0/resources
value:
requests:
memory: 4Gi
limits:
ephemeral-storage: 4Gi
memory: 4Gi
- target:
group: apps
version: v1
kind: StatefulSet
name: argocd-application-controller
patch: |-
- op: add
path: /spec/template/spec/containers/0/resources
value:
requests:
memory: 4Gi
limits:
memory: 4Gi
# rest omitted for brevity...
Disable Admin Account and Add Another Account¶
In the following example we use the configMapGenerator feature of kustomize to modify the argocd-cm configmap to disable the admin account, which comes with Argo-CD by default, and add another account instead.
Note that you would need to activate the alice account using the admin account before disabling the admin account.
apiVersion: kustomize.config.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Kustomization
namespace: argocd
resources:
- github.com/argoproj-labs/argocd-autopilot/manifests/base?ref=v0.4.10
configMapGenerator:
- behavior: merge
name: argocd-cm
literals:
# some keys omitted for brevity...
- admin.enabled=false
- accounts.alice=apiKey, login
Ingress Configuration¶
The following example shows how you would configure ingress using AWS Application Load Balancer. You can easily use this example to configure ingress using other ingress controllers and you can refer to the official Argo-CD documetation for additional information.
Create the argogrpc service:
# /bootstrap/argo-cd/argogrpc.service.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
annotations:
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/backend-protocol-version: HTTP2 #This tells AWS to send traffic from the ALB using HTTP2. Can use GRPC as well if you want to leverage GRPC specific features
labels:
app: argogrpc
name: argogrpc
spec:
ports:
- name: "443"
port: 443
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 8080
selector:
app.kubernetes.io/name: argocd-server
sessionAffinity: None
type: NodePort
Create the ingress resource:
# /bootstrap/argo-cd/ingress.yaml
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
annotations:
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/backend-protocol: HTTPS
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/conditions.argogrpc: |
[{"field":"http-header","httpHeaderConfig":{"httpHeaderName": "Content-Type", "values":["application/grpc"]}}]
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/listen-ports: '[{"HTTPS":443}]'
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/target-type: 'ip'
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/scheme: internet-facing
name: argocd
spec:
rules:
- host: argocd.argoproj.io
http:
paths:
- path: /
backend:
service:
name: argogrpc
port:
number: 443
pathType: Prefix
- path: /
backend:
service:
name: argocd-server
port:
number: 443
pathType: Prefix
tls:
- hosts:
- argocd.argoproj.io
Add the new resources to the kustomization file:
# /bootstrap/argo-cd/kustomization.yaml
apiVersion: kustomize.config.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Kustomization
namespace: argocd
resources:
- github.com/argoproj-labs/argocd-autopilot/manifests/base?ref=v0.4.10
# Added new resources:
- ./ingress.yaml
- ./argogrpc.service.yaml
# rest omitted for brevity...
If ALB is correctly configured on your cluster, the argo-cd application would successfully reconcile after the new ingress resource will be updated with its external address. Then you should be able to reach your Argo-CD through the external address.